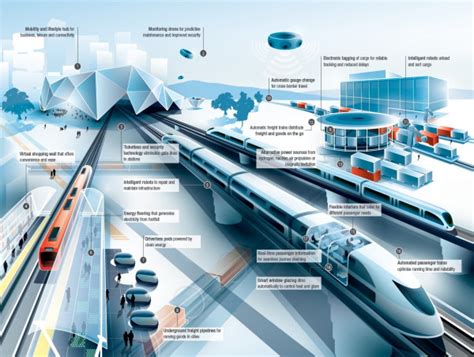
Railways have been a cornerstone of transportation for centuries, connecting cities, countries, and continents like never before. With the advent of technological advancements, the rail industry is poised for a revolution, transforming the way we travel, transport goods, and connect communities. In this article, we'll delve into the exciting world of train tech, exploring the innovations that will shape the future of railways.

Advancements in Train Technology
Trains have come a long way since the steam engine days. Modern trains are equipped with cutting-edge technology, including advanced signaling systems, high-speed propulsion, and sustainable energy sources. Some of the key advancements in train technology include:
- High-Speed Rail: High-speed trains have been operating in several countries for decades, with the most notable being Japan's Bullet Train and France's TGV. These trains can reach speeds of over 300 km/h (186 mph), reducing travel times and increasing efficiency.
- Electric and Hybrid Locomotives: Electric and hybrid locomotives are becoming increasingly popular, offering a more sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional diesel-powered trains. These locomotives use advanced battery technology and regenerative braking to reduce energy consumption.
- Advanced Signaling Systems: Modern signaling systems use advanced software and hardware to optimize train scheduling, reduce delays, and improve safety. These systems enable real-time monitoring and control, allowing for more efficient train operations.
Autonomous Trains: The Future of Rail Safety
Autonomous trains are the latest innovation in rail technology, offering improved safety, efficiency, and reliability. Autonomous trains use advanced sensors, GPS, and artificial intelligence to navigate and control the train, eliminating the need for human intervention. This technology has the potential to reduce accidents, improve punctuality, and increase capacity on busy rail networks.

Sustainable Railways: Reducing Environmental Impact
The rail industry has a significant environmental impact, from energy consumption to noise pollution. To mitigate this impact, the industry is shifting towards more sustainable practices, including:
- Renewable Energy: Many rail operators are investing in renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to reduce their carbon footprint. This includes installing solar panels along rail lines and using wind turbines to generate electricity.
- Energy-Efficient Trains: Modern trains are designed to be more energy-efficient, using advanced materials and aerodynamic design to reduce energy consumption. This includes the use of regenerative braking, which captures kinetic energy and converts it into electrical energy.
- Green Rail Infrastructure: Rail infrastructure is being designed with sustainability in mind, incorporating green roofs, energy-efficient lighting, and rainwater harvesting systems.
Smart Railways: Enhancing Passenger Experience
The rail industry is also focusing on enhancing the passenger experience, using advanced technology to improve comfort, convenience, and accessibility. Some of the key innovations in smart railways include:
- Wi-Fi and Digital Signage: Many rail operators are installing Wi-Fi and digital signage on trains and at stations, providing passengers with real-time information and connectivity.
- Smart Ticketing: Smart ticketing systems use advanced software and hardware to simplify the ticketing process, reducing queues and improving the overall passenger experience.
- Personalized Travel: Rail operators are using data analytics and artificial intelligence to personalize the travel experience, offering tailored recommendations and real-time information.

Revolutionizing Freight Transport: The Future of Rail Logistics
The rail industry is also transforming the way we transport goods, using advanced technology to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase capacity. Some of the key innovations in rail logistics include:
- Automated Freight Handling: Automated freight handling systems use advanced robotics and artificial intelligence to streamline the loading and unloading process, reducing labor costs and improving efficiency.
- Real-Time Tracking: Real-time tracking systems use advanced sensors and GPS to track freight in real-time, improving visibility and reducing delays.
- Intermodal Transport: Intermodal transport systems use advanced software and hardware to optimize the movement of goods between modes of transport, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
Hyperloop: The Future of High-Speed Transport
The Hyperloop is a revolutionary transportation system that uses advanced technology to transport passengers at speeds of up to 1,200 km/h (750 mph). This system uses vacuum-sealed tubes and magnetic levitation to propel vehicles at incredible speeds, reducing travel times and increasing efficiency.

Conclusion
The rail industry is on the cusp of a revolution, driven by advances in technology, sustainability, and passenger experience. From autonomous trains to smart railways, the future of rail transport is exciting and full of possibilities. As the industry continues to evolve, we can expect to see improved safety, efficiency, and sustainability, transforming the way we travel and transport goods.






What is the future of rail transport?
+The future of rail transport is exciting and full of possibilities, driven by advances in technology, sustainability, and passenger experience. From autonomous trains to smart railways, the industry is transforming the way we travel and transport goods.
What is the Hyperloop?
+The Hyperloop is a revolutionary transportation system that uses advanced technology to transport passengers at speeds of up to 1,200 km/h (750 mph). This system uses vacuum-sealed tubes and magnetic levitation to propel vehicles at incredible speeds, reducing travel times and increasing efficiency.
What are the benefits of autonomous trains?
+Autonomous trains offer improved safety, efficiency, and reliability, reducing the risk of accidents and improving punctuality. They also enable real-time monitoring and control, allowing for more efficient train operations.