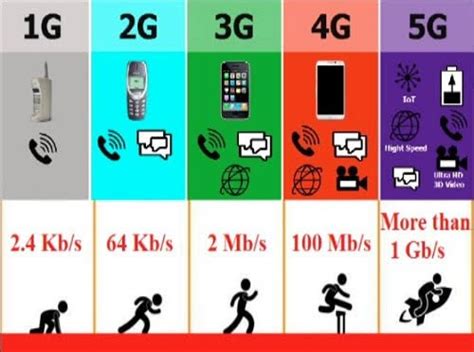
The world of wireless communication has come a long way since the first generation of mobile networks was introduced in the 1980s. We've seen a significant transformation in the way we communicate, access information, and stay connected. The journey from 1G to 5G has been marked by rapid advancements in technology, with each generation building upon the previous one to offer faster speeds, lower latency, and greater connectivity. In this article, we'll delve into the precursors of 5G, specifically 3G and 4G, and explore their features, benefits, and impact on the telecommunications industry.
The Advent of 3G: A New Era in Mobile Communication
The third generation of mobile networks, commonly referred to as 3G, was introduced in the early 2000s. This marked a significant departure from the previous generation, as 3G was designed to support high-speed data transmission and internet access. The main features of 3G networks include:
- Faster data speeds: 3G networks offered data speeds of up to 2 Mbps, a significant improvement over the 2G networks that preceded them.
- Video calling: 3G enabled video calling, allowing users to engage in face-to-face conversations over their mobile devices.
- Mobile broadband: 3G networks provided mobile broadband access, enabling users to access the internet, send emails, and transfer files on the go.
The introduction of 3G revolutionized the way people communicated and accessed information. It paved the way for the widespread adoption of mobile internet and enabled the development of mobile applications that have become an integral part of our daily lives.

The Rise of 4G: Faster Speeds and Greater Connectivity
The fourth generation of mobile networks, commonly referred to as 4G, was introduced in the late 2000s. 4G networks offered faster data speeds, lower latency, and greater connectivity than their 3G predecessors. The main features of 4G networks include:
- Faster data speeds: 4G networks offered data speeds of up to 100 Mbps, a significant improvement over 3G networks.
- Low latency: 4G networks reduced latency to around 50 ms, enabling real-time communication and faster data transfer.
- High-definition video: 4G enabled high-definition video streaming, allowing users to enjoy seamless video playback on their mobile devices.
The introduction of 4G has had a profound impact on the telecommunications industry. It has enabled the widespread adoption of mobile broadband, the development of mobile applications, and the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT).

Comparing 3G and 4G: Key Differences and Similarities
While both 3G and 4G networks offer high-speed data transmission and internet access, there are several key differences between the two technologies.
- Data speeds: 4G networks offer significantly faster data speeds than 3G networks, with average speeds ranging from 10-100 Mbps.
- Latency: 4G networks have lower latency than 3G networks, with average latency ranging from 50-100 ms.
- Capacity: 4G networks have greater capacity than 3G networks, enabling more devices to be connected to the network simultaneously.
Despite these differences, both 3G and 4G networks share several similarities.
- Both 3G and 4G networks offer high-speed data transmission and internet access.
- Both technologies use similar network architecture, including cell towers, base stations, and mobile devices.
- Both 3G and 4G networks support mobile broadband access and enable the development of mobile applications.
The Impact of 3G and 4G on the Telecommunications Industry
The introduction of 3G and 4G networks has had a profound impact on the telecommunications industry. These technologies have enabled the widespread adoption of mobile broadband, the development of mobile applications, and the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT).
- Mobile broadband: 3G and 4G networks have enabled the widespread adoption of mobile broadband, allowing users to access the internet, send emails, and transfer files on the go.
- Mobile applications: The introduction of 3G and 4G has enabled the development of mobile applications, which have become an integral part of our daily lives.
- IoT: The growth of 3G and 4G networks has enabled the development of the Internet of Things (IoT), which is transforming the way we live and work.

The Future of Wireless Communication: 5G and Beyond
As we look to the future, it's clear that wireless communication will continue to play a vital role in our daily lives. The introduction of 5G networks promises to offer even faster data speeds, lower latency, and greater connectivity than its predecessors.
- Faster data speeds: 5G networks are expected to offer data speeds of up to 20 Gbps, a significant improvement over 4G networks.
- Lower latency: 5G networks are expected to reduce latency to around 1 ms, enabling real-time communication and faster data transfer.
- Greater connectivity: 5G networks are expected to enable the widespread adoption of the Internet of Things (IoT), allowing billions of devices to be connected to the network simultaneously.
As we embark on this new era of wireless communication, it's essential to understand the precursors of 5G, specifically 3G and 4G. These technologies have paved the way for the widespread adoption of mobile broadband, the development of mobile applications, and the growth of the Internet of Things (IoT).

Conclusion: The Evolution of Wireless Communication
In conclusion, the evolution of wireless communication has come a long way since the first generation of mobile networks was introduced in the 1980s. From 3G to 4G and now to 5G, each generation has built upon the previous one to offer faster speeds, lower latency, and greater connectivity.
As we look to the future, it's clear that wireless communication will continue to play a vital role in our daily lives. The introduction of 5G networks promises to offer even faster data speeds, lower latency, and greater connectivity than its predecessors.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the precursors of 5G, specifically 3G and 4G. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us.
Gallery of 3G, 4G, and 5G Networks






What is the main difference between 3G and 4G networks?
+The main difference between 3G and 4G networks is the data speed. 4G networks offer significantly faster data speeds than 3G networks, with average speeds ranging from 10-100 Mbps.
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
+The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, allowing them to collect and exchange data.
What are the benefits of 5G networks?
+The benefits of 5G networks include faster data speeds, lower latency, and greater connectivity. 5G networks are expected to offer data speeds of up to 20 Gbps, reducing latency to around 1 ms, and enabling the widespread adoption of the Internet of Things (IoT).