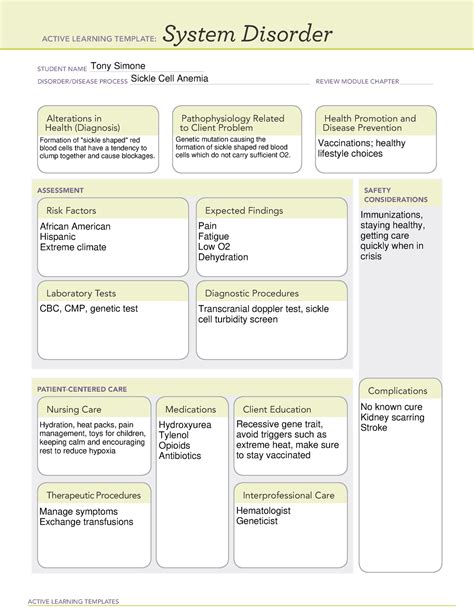
Sickle cell anemia is a genetic disorder that affects hemoglobin production in red blood cells. It is a significant health concern, particularly in communities with African, Middle Eastern, or Mediterranean ancestry. Understanding the condition, its symptoms, and management strategies is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals affected by the disease.
Sickle cell anemia is characterized by the production of abnormal hemoglobin, known as sickle hemoglobin or hemoglobin S. This irregular hemoglobin causes red blood cells to become misshapen, leading to episodes of pain, anemia, and increased infections. The condition can be managed with proper care, but it requires a comprehensive approach that involves medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and emotional support.
Understanding Sickle Cell Anemia
Sickle cell anemia is a genetic disorder that occurs when an individual inherits two mutated hemoglobin genes, one from each parent. The mutated gene codes for abnormal hemoglobin, which causes red blood cells to take on a sickle shape. This irregular shape makes it difficult for red blood cells to pass through small blood vessels, leading to a range of complications.

Symptoms of Sickle Cell Anemia
The symptoms of sickle cell anemia can vary in severity and frequency, but common signs include:
- Episodes of pain, which can range from mild to severe
- Anemia, which can cause fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath
- Increased infections, particularly pneumonia and osteomyelitis
- Delayed growth and development in children
- Vision problems, including blindness
- Increased risk of stroke and other cardiovascular complications
Management Strategies for Sickle Cell Anemia
Managing sickle cell anemia requires a comprehensive approach that involves medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and emotional support. Healthcare professionals should work with patients to develop a personalized care plan that addresses their unique needs and concerns.
- Medical Treatment: Medical treatment for sickle cell anemia typically involves pain management, infection prevention, and blood transfusions. Pain management strategies may include analgesics, anti-inflammatory medications, and other therapies. Infection prevention measures may include antibiotics and vaccinations. Blood transfusions may be necessary to increase red blood cell count and reduce the risk of complications.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Lifestyle modifications can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. Patients should stay hydrated, avoid extreme temperatures, and engage in regular exercise. A balanced diet that includes folic acid and other essential nutrients can also help manage symptoms.
- Emotional Support: Emotional support is critical for individuals with sickle cell anemia. Patients may experience anxiety, depression, and other mental health concerns due to the chronic nature of the condition. Healthcare professionals should provide emotional support and connect patients with mental health resources.
ATI Template Review
The ATI template is a valuable resource for healthcare professionals who care for patients with sickle cell anemia. The template provides a comprehensive framework for assessing, planning, and implementing care. It also includes a review of the condition's pathophysiology, symptoms, and management strategies.

Assessment
Assessment is a critical component of care for patients with sickle cell anemia. Healthcare professionals should assess patients' physical and emotional status, as well as their social and cultural background. The assessment should include a review of the patient's medical history, current symptoms, and laboratory results.
- Physical Assessment: The physical assessment should include a review of the patient's vital signs, including temperature, pulse, and blood pressure. Healthcare professionals should also assess the patient's oxygen saturation, respiratory rate, and cardiac function.
- Emotional Assessment: The emotional assessment should include a review of the patient's mental health status, including anxiety, depression, and other concerns. Healthcare professionals should also assess the patient's coping mechanisms and support systems.
Planning
Planning is an essential component of care for patients with sickle cell anemia. Healthcare professionals should work with patients to develop a personalized care plan that addresses their unique needs and concerns. The plan should include strategies for managing symptoms, preventing complications, and improving quality of life.
- Symptom Management: The care plan should include strategies for managing symptoms, such as pain and anemia. Healthcare professionals should work with patients to develop a pain management plan that includes analgesics, anti-inflammatory medications, and other therapies.
- Complication Prevention: The care plan should include strategies for preventing complications, such as infections and cardiovascular disease. Healthcare professionals should work with patients to develop a plan that includes infection prevention measures, such as antibiotics and vaccinations.
Implementation
Implementation is a critical component of care for patients with sickle cell anemia. Healthcare professionals should work with patients to implement the care plan, which includes symptom management, complication prevention, and lifestyle modifications.
- Symptom Management: Healthcare professionals should work with patients to implement symptom management strategies, such as pain management and anemia treatment.
- Complication Prevention: Healthcare professionals should work with patients to implement complication prevention strategies, such as infection prevention measures and cardiovascular disease prevention.
Evaluation
Evaluation is an essential component of care for patients with sickle cell anemia. Healthcare professionals should evaluate the effectiveness of the care plan and make adjustments as necessary.
- Symptom Management: Healthcare professionals should evaluate the effectiveness of symptom management strategies and make adjustments as necessary.
- Complication Prevention: Healthcare professionals should evaluate the effectiveness of complication prevention strategies and make adjustments as necessary.
Gallery of Sickle Cell Anemia






FAQs
What is sickle cell anemia?
+Sickle cell anemia is a genetic disorder that affects hemoglobin production in red blood cells. It is a significant health concern, particularly in communities with African, Middle Eastern, or Mediterranean ancestry.
What are the symptoms of sickle cell anemia?
+The symptoms of sickle cell anemia can vary in severity and frequency, but common signs include episodes of pain, anemia, increased infections, delayed growth and development in children, vision problems, and increased risk of stroke and other cardiovascular complications.
How is sickle cell anemia managed?
+Managing sickle cell anemia requires a comprehensive approach that involves medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and emotional support. Healthcare professionals should work with patients to develop a personalized care plan that addresses their unique needs and concerns.
We hope this article has provided valuable insights into sickle cell anemia and the ATI template. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to us. We are always here to help.