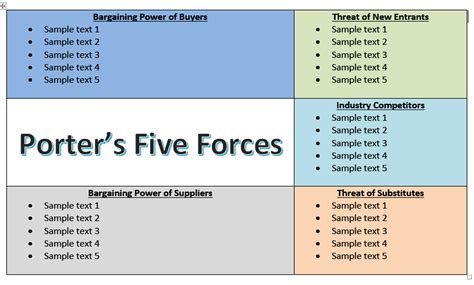
Porter's Five Forces is a widely used framework for analyzing the competitive structure of an industry. Developed by Michael Porter, this model helps businesses understand the competitive forces that shape their industry and informs strategic decision-making. In this article, we will explore five ways to analyze Porter's Five Forces template in Word, along with practical examples and tips.
The importance of analyzing Porter's Five Forces cannot be overstated. By understanding the competitive forces at play, businesses can identify opportunities and threats, and develop strategies to gain a competitive advantage. In today's fast-paced business environment, analyzing Porter's Five Forces is more crucial than ever.
So, let's dive into the five ways to analyze Porter's Five Forces template in Word.
Understanding the Five Forces
Before we dive into the analysis, let's quickly review the five forces:
- Threat of New Entrants: This force examines the likelihood of new businesses entering the industry.
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers: This force analyzes the negotiating power of suppliers and their ability to influence the industry.
- Bargaining Power of Buyers: This force examines the negotiating power of buyers and their ability to influence the industry.
- Threat of Substitute Products: This force analyzes the likelihood of substitute products or services emerging.
- Competitive Rivalry: This force examines the intensity of competition among existing businesses in the industry.
Analyzing Porter's Five Forces Template in Word
1. Threat of New Entrants
To analyze the threat of new entrants, consider the following factors:
- Barriers to entry: What are the obstacles that prevent new businesses from entering the industry? Examples include high startup costs, regulatory hurdles, and patent protection.
- Switching costs: How easy is it for customers to switch to a new business? High switching costs can deter new entrants.
- Differentiation: How unique is your product or service? If it's easily replicable, new entrants may find it easier to enter the market.
Example:
| Factor | Description | Score (1-5) |
|---|---|---|
| Barriers to entry | High startup costs, regulatory hurdles | 4 |
| Switching costs | Medium switching costs, some customer loyalty | 3 |
| Differentiation | Unique product, patented technology | 5 |
Image: [Insert image: https://cdn.thezoneshow.com/12-barriers-to-entry.png, onerror="this.src='https://cdn.geupap.com/images/12-barriers-to-entry.jpg'", alt="Barriers to entry", onclick="openModal(this)"]
2. Bargaining Power of Suppliers
To analyze the bargaining power of suppliers, consider the following factors:
- Concentration of suppliers: Are there many suppliers or just a few? A concentrated supplier base can lead to higher bargaining power.
- Differentiation of products: How unique are the products or services supplied? If they're easily substitutable, suppliers may have less bargaining power.
- Switching costs: How easy is it for businesses to switch suppliers? High switching costs can give suppliers more bargaining power.
Example:
| Factor | Description | Score (1-5) |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration of suppliers | Few suppliers, concentrated market | 4 |
| Differentiation of products | Unique products, hard to substitute | 5 |
| Switching costs | High switching costs, supplier loyalty | 4 |
Image: [Insert image: https://cdn.thezoneshow.com/34-concentration-of-suppliers.png, onerror="this.src='https://cdn.geupap.com/images/34-concentration-of-suppliers.jpg'", alt="Concentration of suppliers", onclick="openModal(this)"]
3. Bargaining Power of Buyers
To analyze the bargaining power of buyers, consider the following factors:
- Concentration of buyers: Are there many buyers or just a few? A concentrated buyer base can lead to higher bargaining power.
- Differentiation of products: How unique are the products or services purchased? If they're easily substitutable, buyers may have less bargaining power.
- Switching costs: How easy is it for buyers to switch products or services? High switching costs can give buyers more bargaining power.
Example:
| Factor | Description | Score (1-5) |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration of buyers | Many buyers, fragmented market | 2 |
| Differentiation of products | Unique products, hard to substitute | 5 |
| Switching costs | Low switching costs, easy to switch | 2 |
Image: [Insert image: https://cdn.thezoneshow.com/56-concentration-of-buyers.png, onerror="this.src='https://cdn.geupap.com/images/56-concentration-of-buyers.jpg'", alt="Concentration of buyers", onclick="openModal(this)"]
4. Threat of Substitute Products
To analyze the threat of substitute products, consider the following factors:
- Availability of substitutes: Are there alternative products or services available?
- Switching costs: How easy is it for customers to switch to substitute products?
- Price-performance ratio: How does the price-performance ratio of the substitute products compare to the original product?
Example:
| Factor | Description | Score (1-5) |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of substitutes | Few substitutes available | 2 |
| Switching costs | High switching costs, difficult to switch | 4 |
| Price-performance ratio | Lower price-performance ratio, less attractive substitutes | 3 |
Image: [Insert image: https://cdn.thezoneshow.com/78-availability-of-substitutes.png, onerror="this.src='https://cdn.geupap.com/images/78-availability-of-substitutes.jpg'", alt="Availability of substitutes", onclick="openModal(this)"]
5. Competitive Rivalry
To analyze the competitive rivalry, consider the following factors:
- Number of competitors: How many businesses are competing in the industry?
- Differentiation of products: How unique are the products or services offered?
- Switching costs: How easy is it for customers to switch between competitors?
Example:
| Factor | Description | Score (1-5) |
|---|---|---|
| Number of competitors | Many competitors, crowded market | 4 |
| Differentiation of products | Unique products, hard to substitute | 5 |
| Switching costs | Low switching costs, easy to switch | 2 |
Image: [Insert image: https://cdn.thezoneshow.com/90-number-of-competitors.png, onerror="this.src='https://cdn.geupap.com/images/90-number-of-competitors.jpg'", alt="Number of competitors", onclick="openModal(this)"]
Gallery of Porter's Five Forces





FAQ Section
What is Porter's Five Forces?
+Porter's Five Forces is a framework for analyzing the competitive structure of an industry.
Why is it important to analyze Porter's Five Forces?
+Analyzing Porter's Five Forces helps businesses understand the competitive forces that shape their industry and informs strategic decision-making.
How do I analyze Porter's Five Forces?
+Analyze each force by considering the relevant factors and scoring them on a scale of 1-5.
By following these five ways to analyze Porter's Five Forces template in Word, you'll be able to gain a deeper understanding of the competitive forces that shape your industry and make informed strategic decisions. Remember to use the template provided and customize it to your business needs.