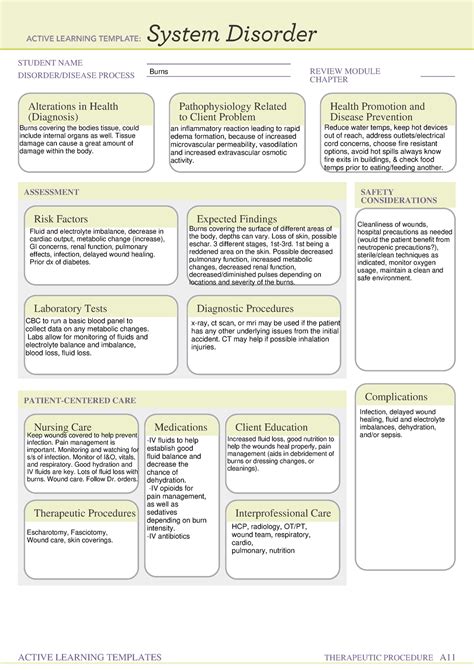
Burns are one of the most devastating injuries a person can experience, with severe burns requiring immediate medical attention to prevent further damage and even death. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 180,000 people die from burns each year. The Burns System Disorder Template And Care Guide is an essential resource for medical professionals and caregivers to ensure the best possible outcomes for burn patients.
Understanding the different types of burns and their severity is crucial for providing effective care. Burns are classified into four categories: first-degree, second-degree, third-degree, and fourth-degree. Each type of burn requires unique treatment and care.
First-Degree Burns
First-degree burns, also known as superficial burns, affect only the outermost layer of skin. They are the mildest form of burns and typically heal within a few days without scarring. Symptoms of first-degree burns include redness, swelling, and pain.

Second-Degree Burns
Second-degree burns, also known as partial-thickness burns, extend into either the papillary dermis or the reticular dermis. They can be further divided into two subcategories: superficial second-degree burns and deep second-degree burns. Superficial second-degree burns affect both the epidermis and the upper part of the dermis, while deep second-degree burns extend into the deeper part of the dermis.

Third-Degree Burns
Third-degree burns, also known as full-thickness burns, extend through all layers of the skin and can damage underlying tissues such as muscle and bone. They are the most severe type of burn and require immediate medical attention.

Fourth-Degree Burns
Fourth-degree burns are the most severe type of burn and extend through all layers of the skin and underlying tissues, including muscle and bone. They are often fatal and require immediate medical attention.

Burn Care
Providing proper care for burns is crucial for promoting healing, preventing infection, and minimizing scarring. Here are some general burn care tips:
- Cool the burn: Run cool tap water over the burn for 10-15 minutes or apply a cool compress.
- Clean the burn: Gently clean the burn with mild soap and water.
- Apply topical creams: Apply topical creams or gels, such as aloe vera or silver sulfadiazine, to help promote healing and prevent infection.
- Cover the burn: Cover the burn with a non-stick dressing or bandage to protect it from further irritation and infection.
Nutrition and Wound Healing
Nutrition plays a critical role in wound healing, including burns. A diet rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals can help promote healing and prevent complications.
- Protein: Protein is essential for building and repairing tissue. Foods rich in protein include lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy products, and legumes.
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C is important for collagen synthesis and wound healing. Foods rich in vitamin C include citrus fruits, strawberries, and leafy green vegetables.
- Zinc: Zinc is essential for wound healing and immune function. Foods rich in zinc include oysters, beef, chicken, and fortified cereals.
Managing Pain and Anxiety
Burns can be extremely painful and cause significant anxiety. Managing pain and anxiety is crucial for promoting healing and improving quality of life.
- Pain management: Pain management is critical for promoting healing and improving quality of life. This can include medication, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, and alternative therapies, such as acupuncture or massage.
- Anxiety management: Anxiety management is also essential for promoting healing and improving quality of life. This can include medication, such as benzodiazepines, and alternative therapies, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises.
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy
Rehabilitation and physical therapy are critical for promoting healing and improving function after a burn injury.
- Range of motion exercises: Range of motion exercises can help promote flexibility and improve function.
- Strengthening exercises: Strengthening exercises can help improve strength and endurance.
- Scar management: Scar management is essential for promoting healing and improving appearance. This can include massage, silicone gel sheeting, and laser therapy.






Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of burns?
+There are four types of burns: first-degree, second-degree, third-degree, and fourth-degree.
How do I care for a burn?
+Cool the burn, clean the burn, apply topical creams, and cover the burn with a non-stick dressing or bandage.
What are some common complications of burns?
+Infection, scarring, and limited mobility are common complications of burns.
In conclusion, burns can be a devastating injury, but with proper care and management, patients can recover and achieve optimal outcomes. By understanding the different types of burns, providing proper care, and managing pain and anxiety, patients can promote healing and improve quality of life.