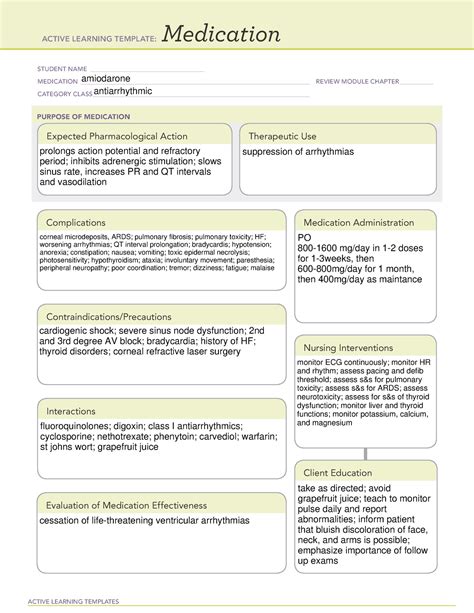
Amiodarone is a powerful antiarrhythmic medication that has been widely used to treat various heart rhythm disorders. As with any medication, it's essential to understand the facts about Amiodarone, including its benefits, risks, and potential side effects. Here are 10 essential facts about Amiodarone ATI medication that you should know.
The Importance of Understanding Amiodarone
Amiodarone is a complex medication that requires careful consideration and monitoring. Patients taking Amiodarone should be aware of its potential benefits and risks, as well as its interactions with other medications. Understanding Amiodarone is crucial for patients to manage their condition effectively and minimize the risk of adverse effects.
What is Amiodarone?

Amiodarone is an antiarrhythmic medication that belongs to the class III antiarrhythmics. It works by prolonging the phase III of the cardiac action potential, which helps to stabilize the heart rhythm and prevent arrhythmias. Amiodarone is available in oral and injectable forms, and it's commonly used to treat various heart rhythm disorders, including atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and ventricular tachycardia.
Benefits of Amiodarone
Amiodarone has several benefits that make it a popular choice for treating heart rhythm disorders. Some of the benefits of Amiodarone include:
-
Effective in Treating Arrhythmias
Amiodarone is highly effective in treating various arrhythmias, including atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and ventricular tachycardia. It works by stabilizing the heart rhythm and preventing arrhythmias.
-
Long-Term Efficacy
Amiodarone has been shown to be effective in the long-term treatment of arrhythmias. Studies have demonstrated that Amiodarone can maintain its efficacy over time, making it a reliable choice for patients with chronic arrhythmias.
-
Low Risk of Proarrhythmic Effects
Unlike some other antiarrhythmic medications, Amiodarone has a low risk of proarrhythmic effects, which means that it's less likely to cause arrhythmias as a side effect.
Risks and Side Effects of Amiodarone
While Amiodarone is generally safe and effective, it can cause several side effects and risks. Some of the common side effects of Amiodarone include:
-
Thyroid Dysfunction
Amiodarone can cause thyroid dysfunction, including hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Patients taking Amiodarone should be monitored regularly for thyroid function.
-
Pulmonary Fibrosis
Amiodarone can cause pulmonary fibrosis, a condition that leads to scarring of the lungs. Patients taking Amiodarone should be monitored regularly for pulmonary function.
-
Liver Damage
Amiodarone can cause liver damage, including cirrhosis and liver failure. Patients taking Amiodarone should be monitored regularly for liver function.
Interactions with Other Medications
Amiodarone can interact with other medications, including:
-
Warfarin
Amiodarone can increase the risk of bleeding when taken with warfarin. Patients taking warfarin and Amiodarone should be monitored regularly for bleeding risks.
-
Digoxin
Amiodarone can increase the levels of digoxin in the body, leading to toxicity. Patients taking digoxin and Amiodarone should be monitored regularly for digoxin levels.
-
Cholestyramine
Amiodarone can decrease the absorption of cholestyramine, leading to reduced efficacy. Patients taking cholestyramine and Amiodarone should be monitored regularly for cholesterol levels.
Contraindications and Precautions
Amiodarone is contraindicated in patients with certain medical conditions, including:
-
Severe Sinus Node Dysfunction
Amiodarone is contraindicated in patients with severe sinus node dysfunction, as it can worsen the condition.
-
Second- or Third-Degree AV Block
Amiodarone is contraindicated in patients with second- or third-degree AV block, as it can worsen the condition.
-
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Amiodarone is contraindicated in pregnancy and breastfeeding, as it can cause harm to the fetus or baby.
Dosage and Administration
The dosage and administration of Amiodarone vary depending on the condition being treated. The typical dosage of Amiodarone is 400-600 mg per day, taken orally or intravenously.

Monitoring and Follow-Up
Patients taking Amiodarone should be monitored regularly for side effects and interactions. Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are essential to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Amiodarone is a powerful antiarrhythmic medication that requires careful consideration and monitoring. Patients taking Amiodarone should be aware of its potential benefits and risks, as well as its interactions with other medications. By understanding Amiodarone, patients can manage their condition effectively and minimize the risk of adverse effects.
Gallery of Amiodarone






Frequently Asked Questions
What is Amiodarone used for?
+Amiodarone is used to treat various heart rhythm disorders, including atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, and ventricular tachycardia.
What are the common side effects of Amiodarone?
+The common side effects of Amiodarone include thyroid dysfunction, pulmonary fibrosis, and liver damage.
Can Amiodarone interact with other medications?
+Yes, Amiodarone can interact with other medications, including warfarin, digoxin, and cholestyramine.
I hope this article has provided you with essential facts about Amiodarone ATI medication. If you have any further questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to ask.