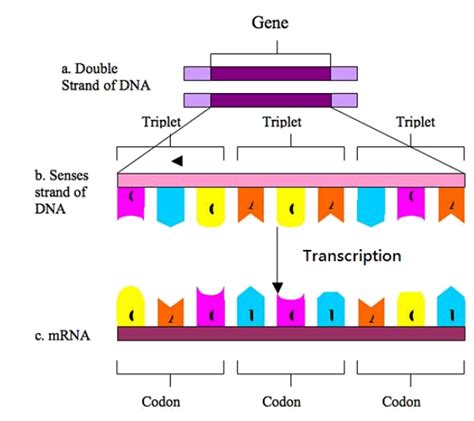
The genetic code is a fundamental concept in molecular biology, and understanding how it works is essential for appreciating the intricacies of life. At the heart of the genetic code is the triplet of bases, a sequence of three nucleotides that determines the genetic information encoded in DNA. In this article, we will explore three ways a triplet of bases works, delving into the mechanisms of gene expression, protein synthesis, and genetic mutation.
The Genetic Code
Before we dive into the workings of a triplet of bases, let's briefly review the genetic code. The genetic code is a set of rules that governs how the sequence of nucleotides in DNA is translated into a sequence of amino acids, which ultimately determines the structure and function of proteins. The genetic code is composed of four nucleotide bases - adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T) - which are arranged in a specific sequence to form a triplet of bases, also known as a codon.
1. Gene Expression
The first way a triplet of bases works is through gene expression. Gene expression is the process by which the genetic information encoded in DNA is converted into a functional product, such as a protein. The triplet of bases plays a crucial role in this process by determining which amino acids are incorporated into the protein sequence.
Here's how it works:
- Transcription: The first step in gene expression is transcription, where the genetic information in DNA is copied into a complementary RNA molecule.
- Translation: The RNA molecule is then translated into a protein sequence, where each triplet of bases (codon) specifies one of the 20 amino acids.
- tRNA molecules: Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules recognize the codons and bring the corresponding amino acids to the ribosome, where they are linked together to form a protein chain.
The triplet of bases is essential for gene expression, as it determines the sequence of amino acids that are incorporated into the protein. Any changes to the triplet of bases can result in changes to the protein sequence, which can have significant effects on the function of the protein.

2. Protein Synthesis
The second way a triplet of bases works is through protein synthesis. Protein synthesis is the process by which the sequence of amino acids is assembled into a functional protein. The triplet of bases plays a crucial role in this process by determining the sequence of amino acids that are incorporated into the protein sequence.
Here's how it works:
- Initiation: The process of protein synthesis begins with the initiation phase, where the ribosome binds to the mRNA molecule and the first amino acid is incorporated into the protein sequence.
- Elongation: The elongation phase involves the sequential addition of amino acids to the protein sequence, where each triplet of bases specifies one of the 20 amino acids.
- Termination: The termination phase occurs when the ribosome reaches the end of the mRNA molecule, and the protein sequence is complete.
The triplet of bases is essential for protein synthesis, as it determines the sequence of amino acids that are incorporated into the protein sequence. Any changes to the triplet of bases can result in changes to the protein sequence, which can have significant effects on the function of the protein.

3. Genetic Mutation
The third way a triplet of bases works is through genetic mutation. Genetic mutation occurs when there is a change in the sequence of nucleotides in DNA, which can result in changes to the protein sequence. The triplet of bases plays a crucial role in this process by determining the sequence of amino acids that are incorporated into the protein sequence.
Here's how it works:
- Point mutations: A point mutation occurs when there is a change in a single nucleotide in the DNA sequence. This can result in a change to the protein sequence, which can have significant effects on the function of the protein.
- Frameshift mutations: A frameshift mutation occurs when there is a deletion or insertion of nucleotides in the DNA sequence, which can result in a change to the protein sequence.
- Silent mutations: A silent mutation occurs when there is a change in the DNA sequence, but it does not result in a change to the protein sequence.
The triplet of bases is essential for genetic mutation, as it determines the sequence of amino acids that are incorporated into the protein sequence. Any changes to the triplet of bases can result in changes to the protein sequence, which can have significant effects on the function of the protein.

In conclusion, the triplet of bases is a fundamental component of the genetic code, and it plays a crucial role in gene expression, protein synthesis, and genetic mutation. Understanding how the triplet of bases works is essential for appreciating the intricacies of life, and it has significant implications for fields such as medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the triplet of bases and its role in the genetic code. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us.
Gallery of Genetic Code





What is the genetic code?
+The genetic code is a set of rules that governs how the sequence of nucleotides in DNA is translated into a sequence of amino acids, which ultimately determines the structure and function of proteins.
What is a triplet of bases?
+A triplet of bases, also known as a codon, is a sequence of three nucleotides that determines the genetic information encoded in DNA.
What is gene expression?
+Gene expression is the process by which the genetic information encoded in DNA is converted into a functional product, such as a protein.